Windows Remote Management is a core technology for the remote management and configuration of Windows machines. WinRM is essential for automating complex Azure and AWS tasks. This guide will outline how to establish WinRM using SSH and a self-signed certificate. A certificate issued from a Certificate Authority would be preferable but for the purpose of establishing a test environment, the steps below are enough to get the technology working.
This demonstration is in three parts.
- Configuring a central “WinRM” server that will be used to remote to client machines
- Creating and exporting a self-signed digital certificate to be used by the clients and server
- Installing the certificate on remote machines.
In a cloud environment you would expect WinRM to be configured with a valid certificate installed within Windows templates. All the commands in this guide are PowerShell based and run from an administrative shell.

Configuring the central WinRM Server
The main body of work on the WinRM server will be the creation of the self-signed certificate. The certificate will be created with PowerShell but as a security measure, the server won’t be setup to listen for incoming WinRM requests nor will the firewall be opened. This configuring step will ensure that the PowerShell Execution Policy allows unsigned scripts to run while ensuring the default HTTP listener is disabled.
The PowerShell commands are:
Set-ExecutionPolicy unrestricted
Enable-PSRemoting –force
winrm quickconfig
winrm set winrm/config/Listener?Address=*+Transport=HTTP `@`{Enabled=`"false`"`}
At this stage, a WinRM compatible certificate needs to be generated.
Creating the Self-Signed WinRM Certificate
A certificate issued from a certificate authority is always preferable to using self-signing. Even so, for development environments or getting your head around WinRM self-signing is a simple solution
Included at the end of this post is a PowerShell script that will generate a self-signed certificate capable of encrypting Windows Remote Management. The certificate must support:
Server Authentication (1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.1)
The certificate must also include the name of the WinRM server in the format “CN=server.mydomain.com” and have exportable private keys. The completed certificate along with private keys will be installed on each client machine.

On Remote Clients
Enable Windows Remote Management
Enable-PSRemoting –force
winrm quickconfig
Configure the Firewall
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name="Windows Remote Management (HTTPS-In)" protocol=TCP dir=in localport=5986 action=allow
Windows Remote Management requires the central server (that will issue WinRM commands) to be trusted. You will need to import the created certificate, disable the HTTP listener, add the central server as a trusted host and create a new listener attached to the imported certificate.
Import Certificates
Manage Computer Certificates -> Personal Store (Local Computer)->All Tasks ->Import
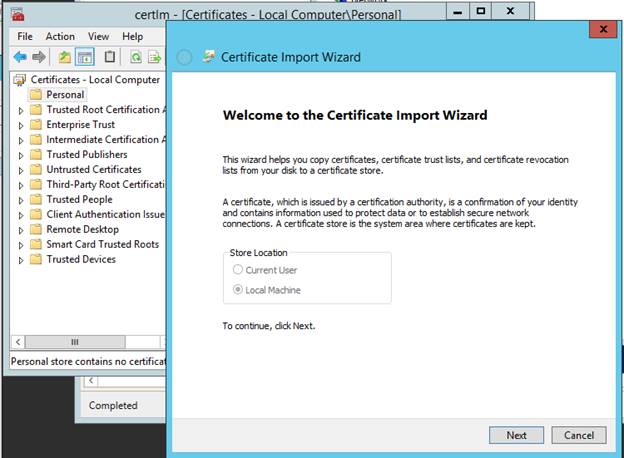
Browse for .pfx file & when prompted enter password
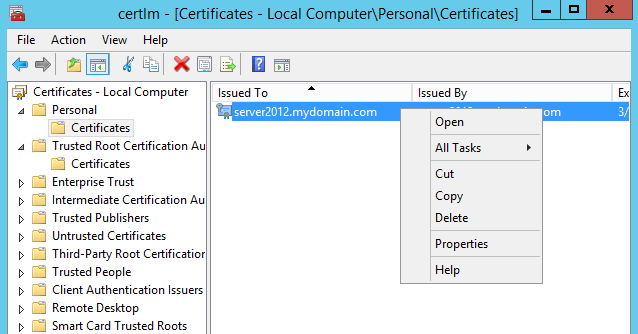
Right-click & copy certificate file. Right-click and paste to the Trusted Root Certificate Authority store.
Configure WinRM
winrm set winrm/config/client `@`{TrustedHosts=`"server.mydomain.com`"`}
winrm set winrm/config/Listener?Address=*+Transport=HTTP `@`{Enabled=`"false`"`}
Create the new listener, substituting the server hostname for your central WINRM server and replacing the certificate thumbprint with the one corresponding to your newly created certificate.
New-Item WSMan:\localhost\Listener -Address * -Transport HTTPS -HostName "server2012.mydomain.com" -CertificateThumbPrint " A5012956A74B05EB1C639428556C0186EXAMPLE7"
Test the Connection from the host / server
Remote PowerShell commands can now be issued from the central server using Invoke-Command.
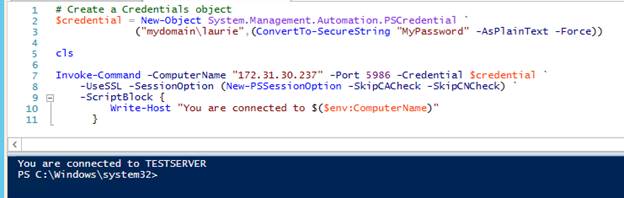
Also note that IP addresses can be used to connect to remote machines. When using a remote credential, local accounts may be used by simply dropping the prepended domain when creating the PowerShell Credential Object
The script below uses Vadims Podans brilliant work for creating a self-signed certificate for authorising WinRM communications. It should be customised to create a unique password for a certificate export and run with Administrative credentials on the intended WinRM server. The resulting certificate (and keys) may be imported on clients.
[[powershell]]
################################################################################################
#
# This script creates a self-signed certificate capable of PowerShell WinRM
#
# Legacy certificate handling used to ensure capability with Windows Server 2008
#
# Version 0.1 6 March 2016 Laurie Rhodes
#
# *** Deserved Credit ***
#
# Primary code leveraged is from Vadims Podans
# (http://en-us.sysadmins.lv/) for certificate creation
####################################################################################>
#region Contributed Community Functions
# Contributors credited with each function
function New-SelfSignedCertificateEx {
#
#####################################################################
# New-SelfSignedCertificateEx.ps1
# Version 1.0
#
# Creates self-signed certificate. This tool is a base replacement
# for deprecated makecert.exe
#
# Vadims Podans (c) 2013
# http://en-us.sysadmins.lv/
#####################################################################
#requires -Version 2.0
.Synopsis
This cmdlet generates a self-signed certificate.
.Description
This cmdlet generates a self-signed certificate with the required data.
.Parameter Subject
Specifies the certificate subject in a X500 distinguished name format.
Example: CN=Test Cert, OU=Sandbox
.Parameter NotBefore
Specifies the date and time when the certificate become valid.
By default previous day date is used.
.Parameter NotAfter
Specifies the date and time when the certificate expires. By default,
the certificate is valid for 1 year.
.Parameter SerialNumber
Specifies the desired serial number in a hex format.
Example: 01a4ff2
.Parameter ProviderName
Specifies the Cryptography Service Provider (CSP) name. You can use
either legacy CSP and Key Storage Providers (KSP). By default
"Microsoft Enhanced Cryptographic Provider v1.0" CSP is used.
.Parameter AlgorithmName
Specifies the public key algorithm. By default RSA algorithm is used.
RSA is the only algorithm supported by legacy CSPs. With key storage
providers (KSP) you can use CNG algorithms, like ECDH. For CNG
algorithms you must use full name:
ECDH_P256
ECDH_P384
ECDH_P521
In addition, KeyLength parameter must be specified explicitly when
non-RSA algorithm is used.
.Parameter KeyLength
Specifies the key length to generate. By default 2048-bit key is
generated.
.Parameter KeySpec
Specifies the public key operations type. The possible values are:
Exchange and Signature. Default value is Exchange.
.Parameter EnhancedKeyUsage
Specifies the intended uses of the public key contained in a certificate.
You can specify either, EKU friendly name (for example
'Server Authentication') or object identifier (OID) value
(for example '1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.1').
.Parameter KeyUsages
Specifies restrictions on the operations that can be performed
by the public key contained in the certificate.
Possible values (and their respective integer values to make
bitwise operations) are:
EncipherOnly
CrlSign
KeyCertSign
KeyAgreement
DataEncipherment
KeyEncipherment
NonRepudiation
DigitalSignature
DecipherOnly
you can combine key usages values by using bitwise OR operation.
when combining multiple flags, they must be enclosed in quotes
and separated by a comma character. For example, to combine
KeyEncipherment and DigitalSignature flags you should type:
"KeyEncipherment, DigitalSignature".
If the certificate is CA certificate (see IsCA parameter), key
usages extension is generated automatically with the following
key usages: Certificate Signing, Off-line CRL Signing, CRL Signing.
.Parameter SubjectAlternativeName
Specifies alternative names for the subject. Unlike Subject
field, this extension allows to specify more than one name.
Also, multiple types of alternative names are supported.
The cmdlet supports the following SAN types:
RFC822 Name
IP address (both, IPv4 and IPv6)
Guid
Directory name
DNS name
.Parameter IsCA
Specifies whether the certificate is CA (IsCA = $true) or
end entity (IsCA = $false) certificate. If this parameter
is set to $false, PathLength parameter is ignored.
Basic Constraints extension is marked as critical.
.PathLength
Specifies the number of additional CA certificates in the
chain under this certificate. If PathLength parameter is
set to zero, then no additional (subordinate) CA certificates
are permitted under this CA.
.CustomExtension
Specifies the custom extension to include to a self-signed
certificate. This parameter must not be used to specify the
extension that is supported via other parameters. In order
to use this parameter, the extension must be formed in a
collection of initialized
System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates.X509Extension
objects.
.Parameter SignatureAlgorithm
Specifies signature algorithm used to sign the certificate.
By default 'SHA1' algorithm is used.
.Parameter FriendlyName
Specifies friendly name for the certificate.
.Parameter StoreLocation
Specifies the store location to store self-signed certificate.
Possible values are: 'CurrentUser' and 'LocalMachine'. 'CurrentUser'
store is intended for user certificates and computer (as well as CA)
certificates must be stored in 'LocalMachine' store.
.Parameter StoreName
Specifies the container name in the certificate store.
Possible container names are:
AddressBook
AuthRoot
CertificateAuthority
Disallowed
My
Root
TrustedPeople
TrustedPublisher
.Parameter Path
Specifies the path to a PFX file to export a self-signed certificate.
.Parameter Password
Specifies the password for PFX file.
.Parameter AllowSMIME
Enables Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions for the certificate.
.Parameter Exportable
Marks private key as exportable. Smart card providers usually do not allow
exportable keys.
.Example
New-SelfsignedCertificateEx -Subject "CN=Test Code Signing"
-EKU "Code Signing" -KeySpec "Signature" `
-KeyUsage "DigitalSignature" -FriendlyName "Test code signing" -NotAfter [datetime]::now.AddYears(5)
Creates a self-signed certificate intended for code signing and which
is valid for 5 years
. Certificate
is saved in the Personal store of the current user account.
.Example
New-SelfsignedCertificateEx -Subject "CN=www.domain.com" `
-EKU "Server Authentication", "Client authentication" `
-KeyUsage "KeyEcipherment, DigitalSignature" -SAN "sub.domain.com","www.domain.com","192.168.1.1" `
-AllowSMIME -Path C:\test\ssl.pfx `
-Password (ConvertTo-SecureString "P@ssw0rd" -AsPlainText -Force) `
-Exportable `
-StoreLocation "LocalMachine"
Creates a self-signed SSL certificate with multiple subject names and
saves it to a file. Additionally, the certificate is saved in the
Personal store of the Local Machine store. Private key is marked as
exportable, so you can export the certificate with a associated private
key to a file at any time. The certificate includes SMIME capabilities.
.Example
New-SelfsignedCertificateEx -Subject "CN=www.domain.com" `
-EKU "Server Authentication", "Client authentication" `
-KeyUsage "KeyEcipherment, DigitalSignature" -SAN "sub.domain.com","www.domain.com","192.168.1.1" `
-StoreLocation "LocalMachine" `
-ProviderName "Microsoft Software Key Storae Provider" -AlgorithmName ecdh_256 `
-KeyLength 256 -SignatureAlgorithm sha256
Creates a self-signed SSL certificate with multiple subject names and
saves it to a file. Additionally, the certificate is saved in the
Personal store of the Local Machine store. Private key is marked as exportable,
so you can export the certificate with a associated private key to a
file at any time. Certificate uses
Ellyptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) key algorithm ECDH with 256-bit key.
The certificate is signed by using SHA256 algorithm.
.Example
New-SelfsignedCertificateEx -Subject "CN=Test Root CA, OU=Sandbox" `
-IsCA $true -ProviderName `
"Microsoft Software Key Storage Provider" -Exportable
Creates self-signed root CA certificate.
#>
[CmdletBinding(DefaultParameterSetName = '__store')]
param (
[Parameter(Mandatory = $true, Position = 0)]
[string]$Subject,
[Parameter(Position = 1)]
[datetime]$NotBefore = [DateTime]::Now.AddDays(-1),
[Parameter(Position = 2)]
[datetime]$NotAfter = $NotBefore.AddDays(365),
[string]$SerialNumber,
[Alias('CSP')]
[string]$ProviderName = "Microsoft Enhanced Cryptographic Provider v1.0",
[string]$AlgorithmName = "RSA",
[int]$KeyLength = 2048,
[validateSet("Exchange","Signature")]
[string]$KeySpec = "Exchange",
[Alias('EKU')]
[Security.Cryptography.Oid[]]$EnhancedKeyUsage,
[Alias('KU')]
[Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates.X509KeyUsageFlags]$KeyUsage,
[Alias('SAN')]
[String[]]$SubjectAlternativeName,
[bool]$IsCA,
[int]$PathLength = -1,
[Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates.X509ExtensionCollection]$CustomExtension,
[ValidateSet('MD5','SHA1','SHA256','SHA384','SHA512')]
[string]$SignatureAlgorithm = "SHA1",
[string]$FriendlyName,
[Parameter(ParameterSetName = '__store')]
[Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates.StoreLocation]$StoreLocation = "CurrentUser",
[Parameter(ParameterSetName = '__store')]
[Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates.StoreName]$StoreName = "My",
[Parameter(Mandatory = $true, ParameterSetName = '__file')]
[Alias('OutFile','OutPath','Out')]
[IO.FileInfo]$Path,
[Parameter(Mandatory = $true, ParameterSetName = '__file')]
[Security.SecureString]$Password,
[switch]$AllowSMIME,
[switch]$Exportable
)
$ErrorActionPreference = "Stop"
if ([Environment]::OSVersion.Version.Major -lt 6) {
$NotSupported = New-Object NotSupportedException `
-ArgumentList "Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 are not supported!"
throw $NotSupported
}
$ExtensionsToAdd = @()
#region constants
# contexts
New-Variable -Name UserContext -Value 0x1 -Option Constant
New-Variable -Name MachineContext -Value 0x2 -Option Constant
# encoding
New-Variable -Name Base64Header -Value 0x0 -Option Constant
New-Variable -Name Base64 -Value 0x1 -Option Constant
New-Variable -Name Binary -Value 0x3 -Option Constant
New-Variable -Name Base64RequestHeader -Value 0x4 -Option Constant
# SANs
New-Variable -Name OtherName -Value 0x1 -Option Constant
New-Variable -Name RFC822Name -Value 0x2 -Option Constant
New-Variable -Name DNSName -Value 0x3 -Option Constant
New-Variable -Name DirectoryName -Value 0x5 -Option Constant
New-Variable -Name URL -Value 0x7 -Option Constant
New-Variable -Name IPAddress -Value 0x8 -Option Constant
New-Variable -Name RegisteredID -Value 0x9 -Option Constant
New-Variable -Name Guid -Value 0xa -Option Constant
New-Variable -Name UPN -Value 0xb -Option Constant
# installation options
New-Variable -Name AllowNone -Value 0x0 -Option Constant
New-Variable -Name AllowNoOutstandingRequest -Value 0x1 -Option Constant
New-Variable -Name AllowUntrustedCertificate -Value 0x2 -Option Constant
New-Variable -Name AllowUntrustedRoot -Value 0x4 -Option Constant
# PFX export options
New-Variable -Name PFXExportEEOnly -Value 0x0 -Option Constant
New-Variable -Name PFXExportChainNoRoot -Value 0x1 -Option Constant
New-Variable -Name PFXExportChainWithRoot -Value 0x2 -Option Constant
#endregion
#region Subject processing
# http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa377051(VS.85).aspx
$SubjectDN = New-Object -ComObject X509Enrollment.CX500DistinguishedName
$SubjectDN.Encode($Subject, 0x0)
#endregion
#region Extensions
#region Enhanced Key Usages processing
if ($EnhancedKeyUsage) {
$OIDs = New-Object -ComObject X509Enrollment.CObjectIDs
$EnhancedKeyUsage | %{
$OID = New-Object -ComObject X509Enrollment.CObjectID
$OID.InitializeFromValue($_.Value)
# http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa376785(VS.85).aspx
$OIDs.Add($OID)
}
# http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa378132(VS.85).aspx
$EKU = New-Object -ComObject X509Enrollment.CX509ExtensionEnhancedKeyUsage
$EKU.InitializeEncode($OIDs)
$ExtensionsToAdd += "EKU"
}
#endregion
#region Key Usages processing
if ($KeyUsage -ne $null) {
$KU = New-Object -ComObject X509Enrollment.CX509ExtensionKeyUsage
$KU.InitializeEncode([int]$KeyUsage)
$KU.Critical = $true
$ExtensionsToAdd += "KU"
}
#endregion
#region Basic Constraints processing
if ($PSBoundParameters.Keys.Contains("IsCA")) {
# http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa378108(v=vs.85).aspx
$BasicConstraints = New-Object -ComObject X509Enrollment.CX509ExtensionBasicConstraints
if (!$IsCA) {$PathLength = -1}
$BasicConstraints.InitializeEncode($IsCA,$PathLength)
$BasicConstraints.Critical = $IsCA
$ExtensionsToAdd += "BasicConstraints"
}
#endregion
#region SAN processing
if ($SubjectAlternativeName) {
$SAN = New-Object -ComObject X509Enrollment.CX509ExtensionAlternativeNames
$Names = New-Object -ComObject X509Enrollment.CAlternativeNames
foreach ($altname in $SubjectAlternativeName) {
$Name = New-Object -ComObject X509Enrollment.CAlternativeName
if ($altname.Contains("@")) {
$Name.InitializeFromString($RFC822Name,$altname)
} else {
try {
$Bytes = [Net.IPAddress]::Parse($altname).GetAddressBytes()
$Name.InitializeFromRawData($IPAddress,$Base64,[Convert]::ToBase64String($Bytes))
} catch {
try {
$Bytes = [Guid]::Parse($altname).ToByteArray()
$Name.InitializeFromRawData($Guid,$Base64,[Convert]::ToBase64String($Bytes))
} catch {
try {
$Bytes = ([Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates.X500DistinguishedName]$altname).RawData
$Name.InitializeFromRawData($DirectoryName,$Base64,[Convert]::ToBase64String($Bytes))
} catch {$Name.InitializeFromString($DNSName,$altname)}
}
}
}
$Names.Add($Name)
}
$SAN.InitializeEncode($Names)
$ExtensionsToAdd += "SAN"
}
#endregion
#region Custom Extensions
if ($CustomExtension) {
$count = 0
foreach ($ext in $CustomExtension) {
# http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa378077(v=vs.85).aspx
$Extension = New-Object -ComObject X509Enrollment.CX509Extension
$EOID = New-Object -ComObject X509Enrollment.CObjectId
$EOID.InitializeFromValue($ext.Oid.Value)
$EValue = [Convert]::ToBase64String($ext.RawData)
$Extension.Initialize($EOID,$Base64,$EValue)
$Extension.Critical = $ext.Critical
New-Variable -Name ("ext" + $count) -Value $Extension
$ExtensionsToAdd += ("ext" + $count)
$count++
}
}
#endregion
#endregion
#region Private Key
# http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa378921(VS.85).aspx
$PrivateKey = New-Object -ComObject X509Enrollment.CX509PrivateKey
$PrivateKey.ProviderName = $ProviderName
$AlgID = New-Object -ComObject X509Enrollment.CObjectId
$AlgID.InitializeFromValue(([Security.Cryptography.Oid]$AlgorithmName).Value)
$PrivateKey.Algorithm = $AlgID
# http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa379409(VS.85).aspx
$PrivateKey.KeySpec = switch ($KeySpec) {"Exchange" {1}; "Signature" {2}}
$PrivateKey.Length = $KeyLength
# key will be stored in current user certificate store
switch ($PSCmdlet.ParameterSetName) {
'__store' {
$PrivateKey.MachineContext = if ($StoreLocation -eq "LocalMachine") {$true} else {$false}
}
'__file' {
$PrivateKey.MachineContext = $false
}
}
$PrivateKey.ExportPolicy = if ($Exportable) {1} else {0}
$PrivateKey.Create()
#endregion
# http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa377124(VS.85).aspx
$Cert = New-Object -ComObject X509Enrollment.CX509CertificateRequestCertificate
if ($PrivateKey.MachineContext) {
$Cert.InitializeFromPrivateKey($MachineContext,$PrivateKey,"")
} else {
$Cert.InitializeFromPrivateKey($UserContext,$PrivateKey,"")
}
$Cert.Subject = $SubjectDN
$Cert.Issuer = $Cert.Subject
$Cert.NotBefore = $NotBefore
$Cert.NotAfter = $NotAfter
foreach ($item in $ExtensionsToAdd) {$Cert.X509Extensions.Add((Get-Variable -Name $item -ValueOnly))}
if (![string]::IsNullOrEmpty($SerialNumber)) {
if ($SerialNumber -match "[^0-9a-fA-F]") {throw "Invalid serial number specified."}
if ($SerialNumber.Length % 2) {$SerialNumber = "0" + $SerialNumber}
$Bytes = $SerialNumber -split "(.{2})" | ?{$_} | %{[Convert]::ToByte($_,16)}
$ByteString = [Convert]::ToBase64String($Bytes)
$Cert.SerialNumber.InvokeSet($ByteString,1)
}
if ($AllowSMIME) {$Cert.SmimeCapabilities = $true}
$SigOID = New-Object -ComObject X509Enrollment.CObjectId
$SigOID.InitializeFromValue(([Security.Cryptography.Oid]$SignatureAlgorithm).Value)
$Cert.SignatureInformation.HashAlgorithm = $SigOID
# completing certificate request template building
$Cert.Encode()
# interface: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa377809(VS.85).aspx
$Request = New-Object -ComObject X509Enrollment.CX509enrollment
$Request.InitializeFromRequest($Cert)
$Request.CertificateFriendlyName = $FriendlyName
$endCert = $Request.CreateRequest($Base64)
$Request.InstallResponse($AllowUntrustedCertificate,$endCert,$Base64,"")
switch ($PSCmdlet.ParameterSetName) {
'__file' {
$PFXString = $Request.CreatePFX(
[Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal]::PtrToStringAuto([Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal]::SecureStringToBSTR($Password)),
$PFXExportEEOnly,
$Base64
)
Set-Content -Path $Path -Value ([Convert]::FromBase64String($PFXString)) -Encoding Byte
}
}
}
#endregion
##############################################################################
# Create-WinRMCert (-FriendlyName "WinRMCert" -ExportPassword "MyPassword")
#
# Creates a self-signed cerificate for use with WinRM
##############################################################################>
function Create-WinRMCert(){
param (
# Create a Unique Friendly Name tag
[Parameter(Mandatory = $false)]
[string]$FriendlyName,
[Parameter(Mandatory = $true)]
[string]$ExportPassword
)
$ipProperties = [System.Net.NetworkInformation.IPGlobalProperties]::GetIPGlobalProperties()
$Hostname = “{0}.{1}” -f $ipProperties.Hostname,$ipProperties.DomainName
$Hostname = $Hostname.ToLower()
# The File location for the exported Certificate
$ExportCertFile = "$($env:TEMP)\$($Hostname).pfx"
If (-NOT ([Security.Principal.WindowsPrincipal] [Security.Principal.WindowsIdentity]::GetCurrent()).IsInRole(`
[Security.Principal.WindowsBuiltInRole] "Administrator"))
{
Write-Warning "Script must be run with Admin Privileges"
Break
}
New-SelfSignedCertificateEx -Subject "CN=$($Hostname)" `
-StoreLocation LocalMachine -StoreName My -FriendlyName $FriendlyName `
-EnhancedKeyUsage @("1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.1") -Exportable -SignatureAlgorithm SHA256
# Create a handle to the certificate
# Note that multiple certificates with the same friendly name could be returned
# We will assume the desired certificate is the first in the returned array
$foundCertArray = get-childitem cert:\LocalMachine\My | where-object {$_.FriendlyName -eq $FriendlyName }
#Export the Certificate - can't rely upon 'Export-Certificate' being available
"Exporting Certificate $($foundCertArray[0].Thumbprint)"
If (Test-Path $ExportCertFile){ Remove-Item $ExportCertFile }
$type = [System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates.X509ContentType]::pfx
[byte[]]$Bytes = $foundCertArray[0].Export($type, $ExportPassword)
[io.file]::WriteAllBytes($ExportCertFile,$Bytes)
Write-Debug "Thumbprint = $($foundCertArray[0].Thumbprint)"
Start-Process -FilePath "C:\Windows\Explorer.exe" -ArgumentList "$($env:TEMP)" } #### Call the example script cls Create-WinRMCert -FriendlyName "WinRMCert" -ExportPassword "MyPassword" [[/powershell]]
Next related blog:
PowerShell DSC - using an IP address to a Workgroup Machine - http://www.laurierhodes.info/?q=node/119
- Log in to post comments